2023.07.28
News
Development of Artificial Blood (Artificial Plasma) for Dogs – Revolution in Veterinary Medicine, Worldwide Market
Abstract
A research group of Professor Teruyuki Komatsu of Chuo University, Faculty of Science and Engineering, has succeeded in developing artificial blood (artificial plasma) for dogs. Blood consists of cell component (blood cells) including erythrocytes, and leucocytes, etc. and fluid component (plasma) including proteins, and vitamins, etc. Albumin*1 is the most abundant plasma protein and plays the two major roles; (i) maintaining the colloid osmotic pressure (COP) and (ii) securing the circulation blood volume. Human serum albumin isolated from donated blood is widely used in the clinical practice. In the case of dogs, however, it is difficult to secure donated blood as a raw material, and thereby no albumin preparation exists for dogs.
In this study, Professor Komatsu’s group has synthesized polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin (POx-PSA) by coupling of synthetic polymer [poly(2-ethyl-2oxazoline)] to serum albumin from porcine plasma. They revealed that the POx-PSA solution can be administered in dogs as an artificial plasma (plasma substitute). Furthermore, the safety and efficacy of POx-PSA were confirmed in collaborations with Keio University, Tokai University, Saitama Medical University, and The University of Tokyo. This breakthrough invention in the pet’s transfusion therapy is expected to make a great contribution in veterinary medicine.
This achievement was published online in Scientific Reports (JST: 2023.6.14), the SPRINGER NATURE’s online scientific journal.
【Researcher】 Teruyuki KOMATSU, Professor of Faculty of Science and Engineering (Department of Applied Chemistry)
【Published Journal】 SPRINGER NATURE, Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 9512:1-15.
Title: “Polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin as an artificial plasma expander for dogs”
【Introduction】
1.Background
Japan is a pet superpower with over 15.9-million domestic dogs and cats; 1) this number far exceeds the population of human children (under the age of 14), 2) The demand for veterinary medicine is increasing year by year because of the aging of animals. Nevertheless, blood transfusion treatment system for dogs and cats have not been established.
The blood consists of blood cells (cell components including erythrocyte, and leucocyte, etc.) and plasma (fluid component including various proteins, and vitamins, etc.) (Figure 1). Albumin is the most abundant plasma protein and plays the two major roles; (i) maintaining the colloid osmotic pressure (COP) and (ii) securing the circulation blood volume. Human serum albumin isolated from donated blood [albumin preparation (fractionated plasma product)] is widely used in the clinical practice. Albumin preparation is administered to patients with decreased albumin production due to liver abnormalities or low albumin level due to kidney abnormality (hypoalbuminemia). It is also used to treat sepsis, refractory ascites associated with liver cirrhosis, refractory edema, and severe burns. As an alternative to albumin, hydroxyethyl starch (HES) preparations are available, but there are risks of side effects, such as blood coagulation disorder, renal dysfunction, and elevated glycolytic enzyme.
On the other hand, no albumin preparation exists for pets (for example, dog albumin preparation obtained from canine blood or cat albumin preparation obtained from feline blood). Pets with hypoalbuminemia can only be given the same species’ blood plasma. However, it is difficult to secure a stable supply of canine and feline plasma. Although, HES preparations are sometimes used, they are immediately excreted from the blood.
2. Contents and Results
“Is it possible to administer albumin from other animals to dogs and cats?” The answer is “No”. For example, porcine serum albumin (PSA) is easily available. Since PSA is a heterogeneous protein for dogs and cats, there is a risk that antibodies will be produced and side effects will occur in the second administration. To avoid this, the protein surface has been modified with a synthetic polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG)*2 to prevent the antibodies formation. PEG is a typical water-soluble polymer with high biocompatibility. However, recent study has found that patients who have administered PEG-conjugated enzyme produced anti-PEG antibodies. In the presence of anti-PEG antibodies, PEG-conjugated preparation is rapidly excreted from the body.
Professor Komatsu and his group have synthesized “polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin (POx-PSA)” by coupling of synthetic polymer, polyoxazoline*3, to porcine serum albumin, and found that it can be administered in dogs as artificial plasma (Figure 2 and 3). Polyoxazoline is also highly biocompatible, non-immunogenic, non-ionic (charge-free) water-soluble polymer. The POx possess superior characteristics features equivalent to PEG, or more.
All these results will not only make a great contribution to the health promotion of pets, but also have a positive ripple effect on entire veterinary medicine and our everyday life. Followings are the essential points of the finding;
・Polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin (POx-PSA) was synthetized by covalently binding of polyoxazoline (molecular weight: 5000) to porcine serum albumin, and its structure was characterized. The manufacturing process is only two steps, synthetic yield is high, and no special equipment is required.
・Lyophilized white powder of POx-PSA can be stored for more than one year. Regenerated POx-PSA solution with water showed identical properties as those of the original solution.
・The POx-PSA solution indicates higher colloid osmotic pressure*4 than PSA solution. This means that the administration of POx-PSA solution shows a superior effect of drawing water from tissues and restoring circulating blood volume.
・The circulation half-life of POx-PSA[15 hours (rats)]was 2.1-fold longer than that of unmodified PSA, implying the long blood circulation persistence.(Collaborations with Tokai University, Saitama Medical University)
・The anti-PSA antibody or anti-POx antibody were not generated after administration of POx-PSA solution to rats. By contrast, the antibodies against PSA and PEG were formed after infusion of PEG-conjugated PSA (PEG-PSA) solution. (Collaboration with Keio University)
・After administration of POx-PSA solution to rats after 50% bleeding of circulating blood volume (hemorrhagic shock model), complete resuscitation was achieved in blood pressure, heart rate, and pH. No abnormality was found in the organs. These results indicate that POx-PSA solution is effective for resuscitation of hemorrhagic shock.(Collaboration with Tokai University, Saitama Medical University)
・POx-PSA solution was administered safely to dogs. (Collaboration with University of Tokyo)
・POx-PSA solution is an artificial plasma which can be administrated not only to dogs but also cats because of its principle of not causing side effects.
3.Further Development
It has long been a dream of veterinary medicine to establish a system in which artificial plasma for dogs and cats is always available as a solution or powder at veterinary hospitals and can be supplied at any time. The market for artificial plasma for pets without fear of viral infection and can respond to mass demand is expected to expand worldwide, including developed and emerging countries.
POx-PSA formulation has a wide range of uses and applications, including protein-losing diseases in dogs (e.g., protein-losing enteropathy, protein-losing nephropathy, hypoalbuminemia, etc.), and acute hypotension caused by bleeding during surgery, etc. This formulation will be extremely effective in emergencies when it is difficult to wait for blood transfusions from donors. POx-PSA is a breakthrough invention which enables the treatment of previously untreatable conditions, and is expected to bring about revolution veterinary medicine.
【Citation data】
1) Japan Pet Food Association, 2022 Nationwide survey on actual conditions in dog and cat breeding https://petfood.or.jp/data/chart2022/index.html
2) Statistics Bureau of Japan, HP(2023.6.12)
https://www.stat.go.jp/data/jinsui/index.html
【Glossary】
*1:albumin
Major simple protein in animal blood plasma. Molecular weight of porcine serum albumin is 66,800. It accounts about 60 percent of entire protein in blood plasma. Its roles are to maintain the colloid osmotic pressure, and preservation and transportation of endogenous and exogenous compounds (metabolic product or drugs etc.)
*2:polyethylene glycol
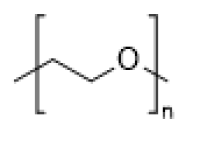
*3:polyoxazoline
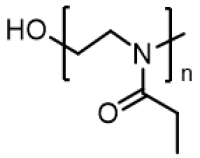
*4:colloid osmotic pressure
The osmotic pressure of plasma which is governed mainly by the concentration of albumin in blood circulation.
【Figures】
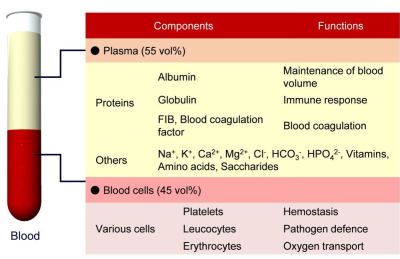
Figure 1. Blood Components
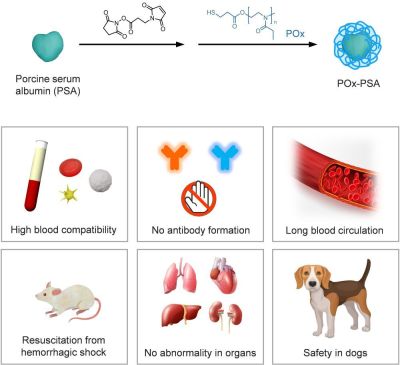
Figure 2. Syntheis and Features of Polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin (POx-PSA)

Figure 3. Polyoxazoline-conjugated porcine serum albumin solution

【Contact】
Teruyuki KOMATSU
Professor of Chuo University, Faculty of Science and Engineering (Department of Applied Chemistry)
E-mail: komatsu★kc.chuo-u.ac.jp
Please replace ★ to @, when sending a mail.
Chuo University, Research Support Office
E-mail: kkouhou-grp★g.chuo-u.ac.jp
Please replace ★ to @, when sending a mail.
